BACnet Explorer - What is the BACnet MSTP network stats page
 Buy the CAS BACnet Explorer:
You can try the BACnet Explorer for free before you buy.
CONTACT US!
Buy the CAS BACnet Explorer:
You can try the BACnet Explorer for free before you buy.
CONTACT US!
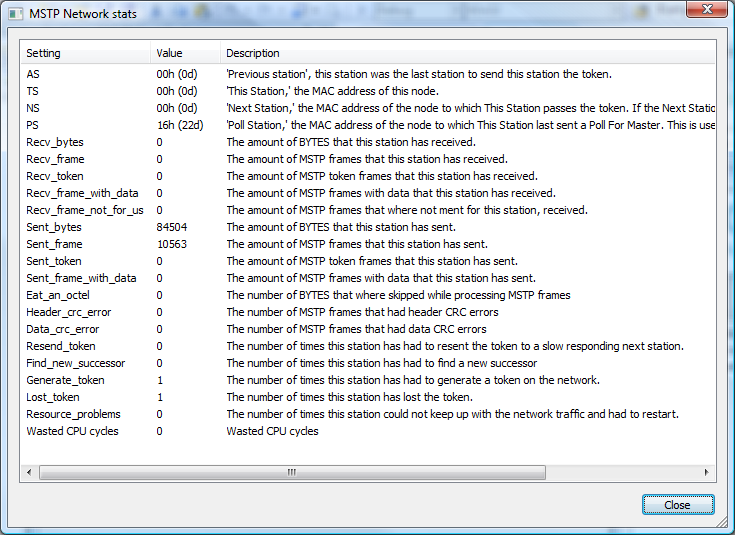
The BACnet MS/TP network statistics page in CAS BACnet Explorer provides detailed runtime information that can be used to diagnose communication issues on a BACnet MS/TP (Master–Slave/Token-Passing) network. This page exposes low-level counters and state information related to frame transmission, token passing, and error conditions.
By reviewing these statistics, engineers and technicians can determine whether the MS/TP network is operating correctly, identify configuration problems, and detect physical-layer issues such as noise or timing mismatches. The information is intended for troubleshooting and validation rather than day-to-day operation.
Purpose of the MS/TP Network Stats Page
BACnet MS/TP networks rely on a token-passing mechanism to control which device is allowed to transmit at any given time. Proper operation depends on correct baud rate configuration, unique MAC addresses, and stable physical wiring. The MS/TP network stats page displays counters and state variables that reflect how well these conditions are being met.
The statistics shown on this page are updated continuously while CAS BACnet Explorer is connected to an MS/TP network. Monitoring how these values change over time provides insight into whether frames are being sent and received correctly and whether the token-passing process is functioning as expected.
Sent and Received Frame Counters
Two of the most basic indicators on the MS/TP network stats page are the Sent_frame and Recv_frame counters. These values track the number of frames transmitted and received by CAS BACnet Explorer on the MS/TP network.
If both counters are increasing steadily, it is a strong indication that communication is active and that the configured baud rate is likely correct. If one or both counters remain static, this may indicate an incorrect baud rate, wiring problem, or that the device is not properly participating in the MS/TP token-passing process.
Poll Station, Next Station, and Token Passing
The MS/TP stats page also displays information related to token passing, including values such as PS (Poll Station), NS (Next Station), and TS (This Station). These values reflect how CAS BACnet Explorer is interacting with other masters on the network.
If the Poll Station value keeps cycling and the Next Station value is equal to the This Station value, CAS BACnet Explorer is attempting to find its next master on the network. This condition commonly occurs when the Explorer’s MAC address is not unique. Each MS/TP device must have a unique MAC address, or token passing will fail.
Performance and Resource Indicators
Counters such as Wasted CPU Cycles, Resource problems, and Lost_token provide insight into whether the host computer running CAS BACnet Explorer can keep up with the MS/TP traffic.
If these values increase over time, it may indicate that the system is struggling to process frames at the configured baud rate or that other applications are consuming excessive system resources. In such cases, reducing network load or adjusting system configuration may be necessary.
Error Counters and Network Noise
Error-related counters such as Header_crc_error and Data_crc_error are used to identify corrupted frames on the MS/TP network. When these values increase alongside Sent and Received frame counters, it often points to electrical noise or wiring issues.
Common causes include improper termination, incorrect grounding, excessive cable length, or interference from nearby electrical equipment. Monitoring these error counters can help isolate physical-layer problems that are not immediately visible through higher-level BACnet diagnostics.
FAQ
What is the BACnet MS/TP network stats page used for?
It is used to diagnose communication, configuration, and physical-layer issues on BACnet MS/TP networks.
Do increasing Sent and Received frame counters indicate correct operation?
Yes. Increasing counters generally indicate active communication and a correct baud rate.
What causes CRC error counters to increase?
CRC errors typically indicate noise, wiring issues, or electrical interference on the MS/TP network.