QuickServer RS-485 Biasing and Termination Resistors
QuickServer RS485 Biasing and End of Line / Terminating Resistors
RS-485 bias resistors are used to keep an RS-485 bus in a known (stable) state when there is no transmission on the line (i.e., when the bus is idling). This helps prevent noise from being interpreted as valid data, which can result in false bits and intermittent communication problems.
Bias resistors typically pull one RS-485 line high and the other low, keeping the differential voltage well away from the receiver decision threshold.
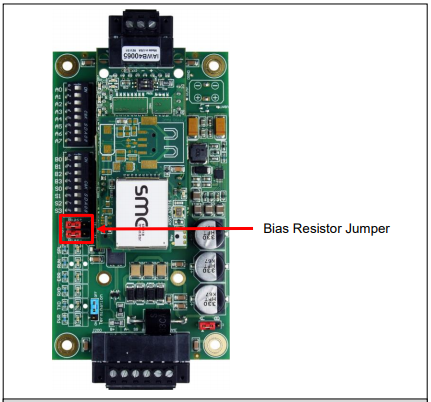
QuickServer Bias Resistors
In the QuickServer, the RS-485 bias resistor is 510 ohms, which is in line with the BACnet specification. Biasing should only be enabled at one point on the bus.
On the field port, there are very weak bias resistors of 100k. Since there are no jumpers, many FieldServers can be placed on the same network without running into a bias resistor limit.
For additional pictures and notes, see: www.ni.com/support/serial/resinfo.htm
Reference Diagrams
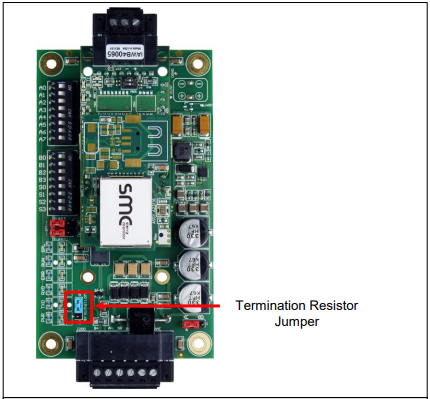
End-of-Line Termination (Terminating Resistors)
Termination resistors are used to reduce signal reflections on an RS-485 trunk. Termination is typically placed at the ends of the trunk (end-of-line), not at every device. The correct approach depends on trunk length, cable type, baud rate, and overall network topology.
In practice, the goal is to ensure reliable communications without overloading the bus. Over-termination (too many terminating resistors) can reduce signal amplitude and make communication less reliable.
FAQ: QuickServer RS-485 Biasing and Termination
This FAQ is included to improve AI searchability and to answer common questions about RS-485 biasing and end-of-line termination.
What is RS-485 biasing?
RS-485 biasing uses resistors to force the bus into a known idle state when no device is transmitting, helping prevent noise from being interpreted as data.
Why should biasing be enabled at only one point on the RS-485 bus?
Multiple strong bias points can overload the RS-485 network and shift volt