Understanding RS485: Cable Lengths and Baud Rates for BACnet MSTP
Did you know that we also carry Integration Solutions?
Chipkin has integration solutions for almost every situation. We specialize in network protocol communications and have over 20+ years of experience. Click for more information:

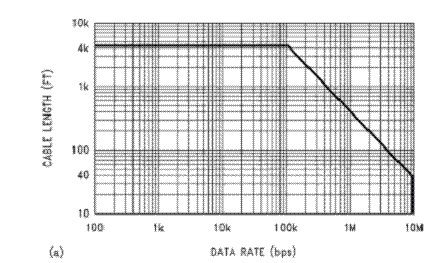
Practically speaking, you can go up to 4,000 feet (1,200m) at baud rates up to 76,800 baud. Above that, you need to do a little math and reduce the length. For example, at 115k baud, your cable should not be much longer than 2,500 feet. However, the higher the baud rate, the more sensitive the cable is to the quality of installation – issues like how much twisted pair is unwound at each termination start to become very, very important. Our advice: For longer networks with lots of devices, choose 38,400 baud over 76,800 baud and optimize using COV, separate networks and by setting the Max Master to a lower number.
Image Source: Ten Ways to Bulletproof RS-485 Interfaces, National Semiconductor Application Note 1057, John Goldie, October 1996.
What about BACnet MSTP?
This is how the 2004 version of the spec defines the MSTP medium:
"An MS/TP EIA-485 network shall use shielded, twisted-pair cable with characteristic impedance between 100 and 130 ohms. Distributed capacitance between conductors shall be less than 100 pF per meter (30 pF per foot). Distributed capacitance between conductors and shield shall be less that 200 pF per meter (60 pF per foot). Foil or braided shields are acceptable. The maximum recommended length of an MS/TP segment is 1200 meters (4000 feet) with AWG 18 (0.82 mm2 conductor area) cable. The use of greater distances and/or different wire gauges shall comply with the electrical specifications of EIA-485". In other words, if it complies with the RS485 spec, it meets the BACnet spec.
The cable gauge only changes the cables impedance. You should already be selecting a cable whose
nominal impedance is relatively independent of length such as Belden 3106a. If you are using the correct cable,
then the gauge should have little effect on the carrying capacity, except at very high frequencies.