Use of wireshark to decode BACnet traffic on non standard ports
Use of Wireshark to Decode BACnet Traffic on Non-Standard Ports
BACnet/IP traffic is commonly assumed to operate on the default UDP port 47808 (hexadecimal 0xBAC0). In practice, however, BACnet/IP can operate on any UDP port. Many real-world systems intentionally use non-standard ports due to firewall rules, network segmentation policies, NAT traversal, or vendor-specific deployment practices.
Chipkin frequently encounters BACnet/IP traffic operating on port ranges such as 47808–47817 (hexadecimal BAC0–BAC9), but it is not uncommon to see completely different UDP ports in secured or routed environments. When this happens, packet capture tools such as Wireshark will no longer automatically decode the traffic as BACnet/IP.
This article explains how to manually instruct Wireshark to decode BACnet/IP traffic correctly when it is transmitted on a non-standard UDP port. This technique is essential when troubleshooting BACnet communication issues, validating protocol behavior, or analyzing traffic captured from gateways, routers, or field devices.
Why Wireshark Does Not Decode Non-Standard BACnet Ports Automatically
Wireshark determines how to decode network traffic based on a combination of protocol signatures and well-known port assignments. By default, Wireshark associates BACnet/IP decoding with UDP port 47808. If BACnet/IP traffic appears on any other port, Wireshark will treat it as generic UDP data unless instructed otherwise.
This does not indicate a problem with the BACnet device or the captured traffic. It simply means that Wireshark requires manual configuration to associate the selected UDP port with the BACnet/IP protocol stack.
Instructions
- Start Wireshark.
- Load an existing capture file or begin capturing network traffic that includes BACnet/IP packets operating on a non-standard UDP port.
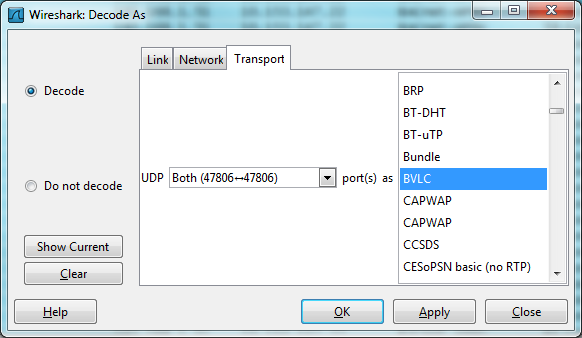
- From the Analyse menu, select Decode As….
- In the Decode As dialog, locate and select the non-default UDP port number used by the BACnet/IP traffic from the drop-down list.
-
In the protocol selection column, choose BVLC.
Note: BVLC stands for BACnet Virtual Link Control and represents the transport-layer header used by all BACnet/IP messages. - Click OK to apply the change.
Once this mapping is applied, Wireshark will immediately begin decoding packets on the selected UDP port as BACnet/IP, allowing you to inspect NPDU, APDU, services, objects, and properties as expected.
Common Troubleshooting Notes
When decoding BACnet/IP on non-standard ports, keep the following practical points in mind:
- The Decode As setting applies only to the selected capture session or file. If you open a new capture, you may need to reapply the mapping.
- If multiple BACnet/IP ports are in use, each port must be explicitly mapped to BVLC in Wireshark.
- This technique works for both live captures and offline PCAP analysis.
- If packets still do not decode correctly, confirm that the traffic is truly BACnet/IP and not BACnet/MSTP encapsulated by another transport.
Proper decoding is a prerequisite for meaningful BACnet analysis. Without it, higher-layer protocol fields such as service choice, object identifiers, and property values will not be visible.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Why would BACnet/IP use a non-standard UDP port?
Non-standard ports are often used to satisfy firewall rules, avoid port conflicts, isolate traffic, or comply with site-specific security policies. Some vendors and integrators also choose alternate ports for routing or NAT scenarios.
Does changing the Decode As setting affect the actual network traffic?
No. Decode As only affects how Wireshark interprets captured packets. It does not modify traffic on the network or alter device behavior.
Is BVLC always the correct protocol to select?
Yes. BVLC is the correct top-level protocol for BACnet/IP traffic and must be selected for Wireshark to decode BACnet/IP packets correctly.
Can this be used for routed or BBMD traffic?
Yes. This technique applies equally to routed BACnet/IP traffic, BBMD environments, and foreign device registration scenarios, as long as the traffic is BACnet/IP.
What if the traffic still does not decode after using Decode As?
Verify the UDP port number, confirm that the traffic is BACnet/IP (not MSTP or another protocol), and ensure the capture includes complete packets. Encrypted or malformed traffic may also prevent proper decoding.