RS-485 Cable Selection for BACnet MS/TP Networks
 CAS BACnet Explorer:
Available as a free tool for discovering, browsing, and testing BACnet devices.
CAS BACnet Explorer:
Available as a free tool for discovering, browsing, and testing BACnet devices.
BACnet MS/TP networks are most commonly implemented over RS-485, a balanced differential signaling standard designed for multi-drop serial communication. While RS-485 is tolerant of noise and distance compared to single-ended signaling, physical layer characteristics such as cable impedance, capacitance, shielding, and grounding still have a direct impact on network reliability.
Cable selection becomes increasingly important as trunk length, device count, and baud rate increase. Improper cable characteristics can lead to signal reflections, timing errors, intermittent communication, and token passing failures on MS/TP networks.
Impedance and Termination Considerations
All cables exhibit characteristic impedance. For RS-485 and BACnet MS/TP, cables with a controlled and distance-independent characteristic impedance are preferred. These cables typically specify a nominal impedance value (for example, 100 Ω or 120 Ω) rather than an impedance value per unit length.
If a cable specification lists impedance as a single nominal value, it is generally suitable for RS-485 applications. If impedance is expressed per meter or per foot, the cable is not designed as a controlled- impedance transmission line. In such cases, determining appropriate termination resistor values becomes more complex and may require measurement and calculation.
In addition to impedance, low capacitance is desirable. High capacitance increases signal rise and fall times, which can degrade communication margins at higher baud rates or over longer distances.
Use of Category Cable (Cat5/Cat5e)
Category cable such as Cat5 or Cat5e can be used for BACnet MS/TP in many installations. These cables have controlled impedance and twisted pairs, which are beneficial for differential signaling.
When using Cat5-type cable, one twisted pair should be used for the RS-485 differential signals (Tx/Rx+ and Tx/Rx-). A conductor from another pair should be used as the signal ground or reference. Consistent pairing and grounding practices should be maintained across the entire trunk.
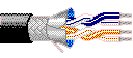
Example RS-485 Cable Types
The following cable types are commonly used in industrial RS-485 and BACnet MS/TP installations and are designed with suitable impedance, shielding, and conductor characteristics.
Belden 3106A
Belden 3107A
Multi-Conductor – EIA Industrial RS-485 PLTC/CM
22 AWG stranded (7×30) tinned copper conductors, Datalene® insulation, twisted pairs, overall foil
shield (100% coverage) with tinned copper braid (approximately 90% coverage), drain wire, and a UV-resistant
PVC jacket.
FAQ
Does cable selection affect BACnet MS/TP reliability?
Yes. Cable impedance, capacitance, and shielding directly affect signal integrity, especially on longer
trunks and at higher baud rates.
Is termination always required?
Proper termination is required at the physical ends of an MS/TP trunk. Correct cable impedance simplifies
termination selection and improves signal stability.
Can mixed cable types be used on the same trunk?
Mixing cable types is not recommended, as differing impedance and capacitance characteristics can introduce
reflections and unpredictable behavior.
Why is low capacitance important?
Lower capacitance reduces signal distortion and timing issues, improving communication margins across the
network.