What is BACnet BBMD? Hardware and Software Solutions
Introduction to Chipkin's 2 BBMD Solutions
Chipkin provides advanced solutions for BACnet BBMD. Anything that prevents broadcasts also prevents BACnet communication leading to substantial challenges for BACnet Networks. Chipkin's CAS BACnet BBMD, a Windows and Linux tool, is a complementary product to Chipkin's on-device BBMD operating on the FieldServer platform's QuickServer Protocol converter and BACnet Router line of products. These BBMDs efficiently manage BACnet messages across routers and subnets, supporting both BDT and FDT.
Unlike the on-device BBMD, The CAS BACnet BBMD (BACnet Broadcast Management Device) is a Windows and Linux software application that allows multiple BACnet/IP devices to send BACnet broadcast messages across NAT routers, and BACnet/IP devices with different IP/UDP ports to communicate with each other.
BACnet/IP uses IP/UDP broadcast messages to communicate on local subnet. If two BACnet/IP devices are on different subnetworks (VLans, NAT Routers, etc…) and need to communicate with each other, a BBMD device is needed to facilitate sending and rebroadcasting the messages on the different subnetworks.
What is BACnet BBMD and what does it solve?
BACnet BBMD services act as mediators, similar to marriage counseling, facilitating communication between BACnet networks much like a counselor aids in resolving conflicts between partners.

BACnet discovery uses two services - one is called ‘Who-Is’ and the other ‘I-Am’. They rely on the use of broadcasts.
Routers join IP networks together so that messages from one network can be sent to another. Most routers do not forward broadcast messages and this means discovery can't discover devices on another network.
To solve this problem, BACnet provides a technology called BBMD - BACnet/IP Broadcast Management Device.
Overall, the technology is simple. You install a BBMD (might be a physical device or a software application on a computer) on each network. You can configure the BBMD by specifying the IP Address and mask of each BBMD. This makes both BBMD configs identical. When one BBMD receives a broadcast, it forwards the messages to the other BBMD, which in turn re-broadcasts on the other network. They are configured by BDT files and these may be modified on the fly using select Bacnet services.
The technology also provides for foreign device registration. This allows a device on one network to communicate with a device on another network by using the BBMD to forward and route the messages.
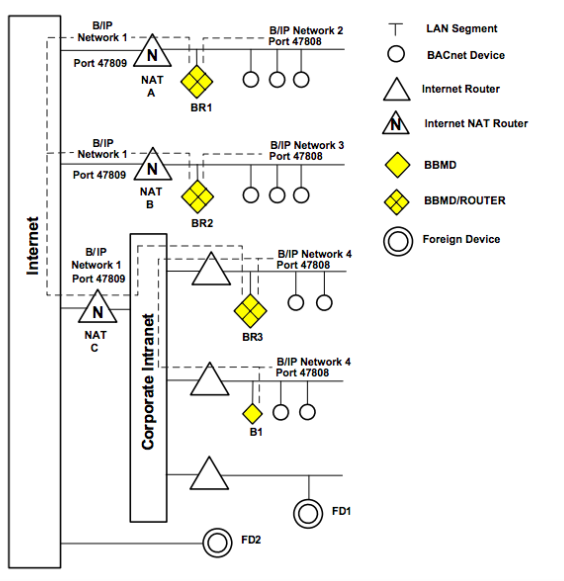
BBMD Network Diagram
Below is a network diagram that shows where BBMD devices can be used on a common BACnet network.
System Specifications
List all BACnet Interoperability Building Block Supported (BIBBs Annex K):
- DS-RP-B - Data Sharing - ReadProperty - B
- DM-DOB-B - Device Management - Dynamic Object Binding - B
- NM-RC-B - Network Management - Router Configuration - B
- DS-RPM-B - Data Sharing - ReadPropertyMultiple - B
- DM-DDB-B - Device Management - Dynamic Device Binding - B
- NM-BBMDC-B - Network Management - BBMD Configuration - B
Requirements:
- OS: Windows 7, 10 or Linux Ubuntu
- Hard Drive: 50mb
BACnet Standardized Device Profile (Annex L):
- BACnet Broadcast Management Device (B-BBMD)
Data Link Layer Options:
- BACnet IP, (Annex J) BACnet Broadcast Management Device (BBMD)
- BACnet IP, (Annex J), Network Address Translation (NAT Traversal)
Case Study - BACnet on Segmented Networks using Chipkin's BBMD
A university has several buildings. Each building has several BACnet/IP sensors in them. A central control room that monitors all the buildings' sensors using an HMI. The university has segmented the buildings into their own VLANs where each building has a different subnet. When the HMI tries to discover the BACnet/IP device across the university campus it sends out a IP/UDP broadcast.
The IP/UDP broadcasts are not routed through the NAT routers and HMI can not discover any of the other BACnet/IP devices on the different VLANs or subnetworks.
The solution is to install and configure a BBMD device on each VLAN and ...
To read the full case study, Click Here!
University Use Case Example
A university has several buildings. Each building has several BACnet/IP sensors in them. A central control room that monitors all the buildings' sensors using an HMI. The university has segmented the buildings into their own VLANs where each building has a different subnet. When the HMI tries to discover the BACnet/IP device across the university campus it sends out a IP/UDP broadcast. The IP/UDP broadcasts are not routed through the NAT routers and HMI can not discover any of the other BACnet/IP devices on the different VLANs or subnetworks.
The solution is to install and configure a BBMD device on each VLAN and subnetwork. The BBMD device receives the IP/UDP broadcast message and relays it to the other BBMD devices on different VLANs or subnetworks networks through a directed IP/UDP message. When a BBC receives a directed message from another BBMD it will broadcast the message on its local network VLAN/Subnet. The communication is bidirectional so devices on the VLANs and subnets can communicate to the HMI via the BBMDs as well.
This allows a central HMI to communicate with all the BACnet/IP devices in the different segregated buildings/VLANs/Subnets.
Available BACnet Tools
BACnet for Field Technicians (Free!)
Learning about BACnet? Want to update your BACnet knowledge? This free EBook will guide you through basic and advanced BACnet topics.
You can purchase a hardcopy of this book from Amazon or you can download the BACnet for Field Technicians for free from our website.
