RS-485 Trunk Capacity: Recommended Device Counts
Introduction
This article describes when and how RS-485 networks can be designed to support more than 32 devices, including segmentation approaches, repeaters, and protocol limitations that enable scaling beyond traditional device counts.
For basic planning and recommended device counts on RS-485 trunks, see RS-485 Trunk Device Count Guidelines.
At Chipkin, we get questions like these all the time. The answer almost always contains the words "it depends". In this article, we will explore the different variables we've encountered to help you make the right decision for your network.
- "I have 300 energy meters - How many gateways will I need?"
- "I have 1,000 MS/TP devices - What is an optimal design?"
- "I have dozens of different types of devices to connect - How many different gateways will I need?"
Theoretical Maximum Number of Devices on a Trunk
RS-485 does not specify the maximum number of bus connections. Instead, the standard defines the steady-state electrical load presented by a bus connection in Unit Loads. The following paragraphs explain the Unit Load and how it is used to determine the maximum number of nodes connected to an RS-485 bus segment.
- The Unit Load is a relative parameter that provides a basis for determining the maximum number of connections to an RS-485 bus segment or specifying the input characteristics of line circuits. A standard RS-485 driver will handle 32 Unit Loads that could consist of 256 one-eighth Unit-Load devices.
How much load does your energy meter / chiller / sensor present to the RS485 trunk? This is the key question. The answer is, unfortunately, almost impossible to find. Most vendors do not provide this information. The theoretical limit = 256 devices that 1/8th load each. If you need to be certain and you do not know how much load the devices present then assume a full load and thus the maximum = 32 devices at full load.
Most RS485 devices use off the shelf RS485 chips inside their devices. You can reasonably assume that if your device is from a major manufacturer - and is less than 10 years old - that each device presents less than a full load. Eg. MAX1482/MAX1483 present 1/8th Load.
Keep in Mind: If you have devices that date back to the 80's and 90's you are probably best assuming each device presents a full load and thus you should have no more than 32 devices on the trunk.
Bandwidth / Latency Issues
HVAC is a slow automation because temperatures change slowly. However, some processes - like extruding steel - are very fast. Some automations are very time sensitive to the freshness of the data. This is something you need to think about in planning your RS485 networks. How up to date must the data be?
2 Wire RS485 is a poll-response technology which only allows one device to be active at any time. RS485 is not very fast. Common baud rates are 9600,19200,38400 and 76800 baud. That roughly converts to 960 bytes per second, 1920 bytes per second etc.

How many devices should I install on a single RS485 Trunk? (Bandwidth Issues).
Consider the following factors.
- A single Modbus message can only read consecutive data points. If you need to read 40001 and 40003 you
must either:
- read 40001 length=3
- read 40001 length=1 and read 40003 length =1 (2 messages and 2 responses)
- A single Modbus message cannot read more than 125 16-bit words:
- The more dispersed the Modbus points you are reading, the more messages and responses you will need. For example. If you need to read 40001 and 40128 then you will need at least two messages because all the data cannot be read in one message.
- Some devices have more severe limits. For example, Crestron can only read 8 registers at a time.
- A single Modbus message can only read data of one type
- If you need to read a coil and a holding register you will need at last one message for each.
- What is the baud rate?
- Divide the baud rate by 10 to get approx. characters per second.
- Divide the result by 2 to get approx. number of words per second.
- Thus, at 19200 baud it takes approx. to read 125 registers.
- Poll = 10 bytes at 1920 per sec
- Server latency
- Response = 125 words at 960 per sec.
- Client Latency (delay in storing response and sending next)
- Approx 0.15 secs to .35 secs with typical latencies.
Cables - Types & Quality of Installation
3 Wires, not 2- RS485 is a 3 conductor network. You take a huge risk by not installing the 3rd conductor. You risk blowing 485 ports, you risk unstable operation (works sometimes and doesn't work other times) and finally you risk re-installation. For a more detailed discussion WHY YOU NEED 3 WIRES FOR 2 (TWO) WIRE RS485 FOR BACNET. The more power sources used to power devices, the greater the physical separation of devices, the less well grounded devices and power sources are - the greater the risk.

Remember this statement: The so called Ground Terminal on a RS485 interface is not a connection to ground. It is a common reference signal. The voltage level on the Tx/Rx conductors are measured relative to this voltage level. You can (if you must) use a shield drain wire as the 3rd conductor (ground reference conductor).
All cables offer impedance (resistance). Some cables are designed so that the impedance is relatively independent of distance. You want one of these cables. A clue to knowing if you selected one is to look at the cable's Nominal Impedance. If they quote a number such a 100Ohms you have a good cable. If they quote an impedance per meter/foot you have chosen the wrong kind. Wrong in the sense – to determine the value of terminating resistors now requires measurements and calculations. Choose low capacitance cables. Can you use Cat5 cable? Yes. Use one pair for Tx,Rx and a conductor from another pair for the ground reference signal.
We Recommend These Cables

Belden 3106A
- Multi-Conductor - EIA Industrial RS-485 PLTC/CM 22 AWG stranded (7x30) tinned copper conductors.
- Datalene® insulation, twisted pairs, overall Beldfoil® shield (100% coverage) plus a tinned copper braid (90% coverage), drain wire, UV resistant PVC jacket.
Belden 3107A
- Multi-Conductor - EIA Industrial RS-485 PLTC/CM 22 AWG stranded (7x30) tinned copper conductors.
- Datalene® insulation, twisted pairs, overall Beldfoil® shield (100% coverage) plus a tinned copper braid (90% coverage), drain wire, UV resistant PVC jacket.
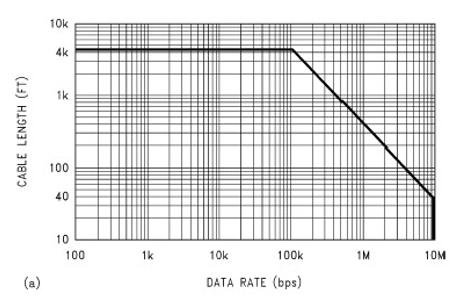
Cable Lengths and Baud Rates
Practically speaking, you can go up to 4000 feet at baud rates up to 76800 baud. Above that you need to do a little math and reduce the length. For example, at 115k baud your cable should not be much longer than 2500 feet. However, the higher the baud rate the more sensitive the cable is to the quality of installation – issues like how much twisted pair is unwound at each termination start to become very important.
Our Advice: For longer networks with lots of devices, choose 38k400 baud over 76k800 baud and optimize using COV, separate networks and by setting the Max Master to a lower number.
Best & Worst RS485 Topologies
We recommend minimizing the untwisting of the twisted pairs – this is very important for high baud rates but relatively unimportant at typical RS485 baud rates. However, with long trunks and many devices, every single aspect of the quality of installation counts.
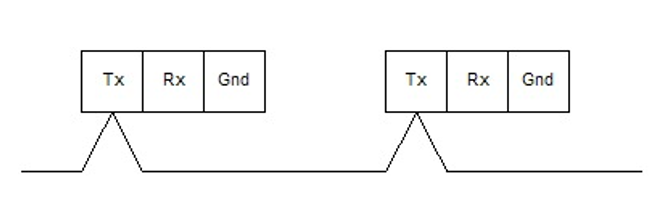
Best RS485 Arrangement. (TX conductor for reference only)
Take care with the topology. The best topology is a single trunk that in-outs on the terminal blocks of each device it connects. What do we mean by "best"? We mean the choice which is least likely to cause problems.
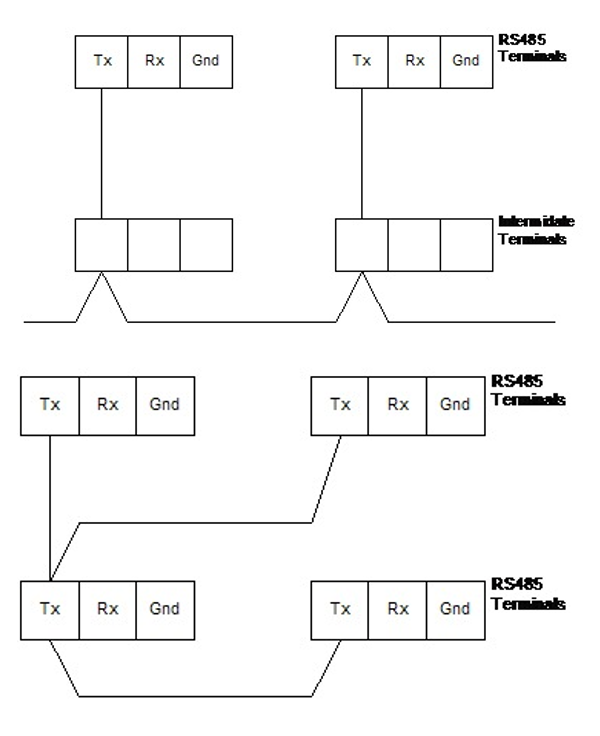
Worst RS485 Topologies - Avoid At All Costs
Getting worse. Making the connections to the RS485 terminals, drops instead of connections starts to give the electrical signals all kinds of complicated paths for reflections and harmonics. It is obvious that if the drops are long and are not twisted then you also have more chance to induce noise. (Showing TX conductor for reference only).
Did you know that we also carry Integration Solutions?
Chipkin has integration solutions for almost every situation. We specialize in network protocol communications and have over 20+ years of experience. Click for more information:


