Power Line Communication
Types of Power Line Communication
Power Line Communication (PLC) is also known as power line carrier, power-line digital subscriber line (PDSL), power line telecom (PLT), power line networking (PLN), mains communication, and broadband over power lines (BPL).
Four Major Types
- In-house networking: High-speed data transmission can be provided for home networking using the in-house mains power wiring.
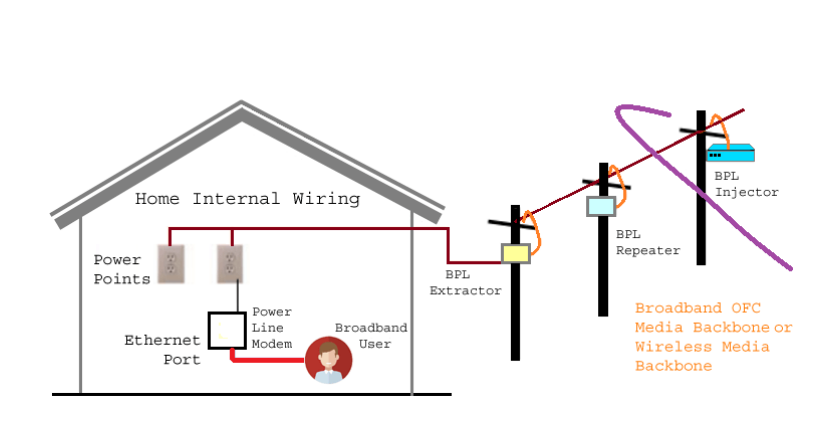
- Broadband over Power Line: Broadband internet access offered through the outdoor mains power wiring.
- Narrowband in-house applications: Home automation and intercoms controlled and used for communication through the in-house power mains.
- Narrowband outdoor applications: Used for automatic meter reading and remote surveillance or control.
Working Mechanism
Power Line Communication consists of a sender (modulates data), communication medium, and a receiver (demodulates data).
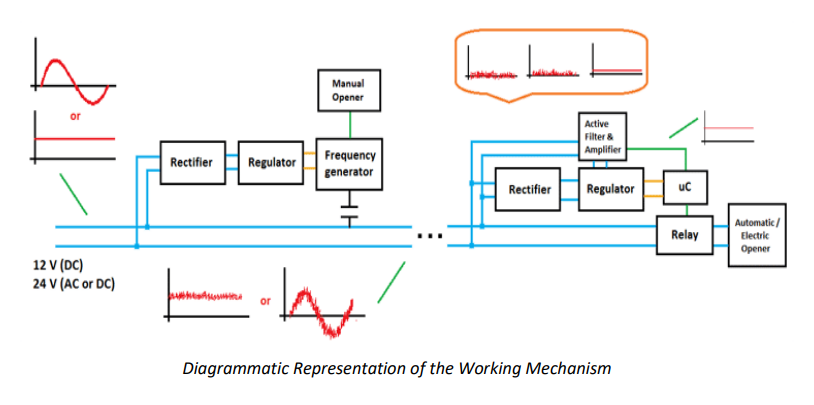
PLC also allows the user to control and monitor all the connected devices to the power line since it is implemented in the same wiring system. PLC incorporates a Rectifier with a Filter thus sending a less fluctuating signal. It uses a Microcontroller and a relay switch for the transmission of data which is more accurate and stable with good output signals.
Modulation Schemes Used in Power Line Communications
"Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM), Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK), Frequency Shift Keying (FSK), Spread-FSK (S-FSK) and proprietary schemes too (like the Differential Code Shift Keying (DCSK)) are the modulation schemes used in PLC.
OFDM provides high data rates but requires good computational horsepower for Fast Fourier Transforms (FFT) and Inverse-FFT (IFFT) output. On the other hand, BPSK, FSK are quite standard and simple modulation schemes that can be used in PLC but they offer low data rates.
The currently running modulation scheme for PLC is OFDM with PSK modulation that can handle such a heavy computation."
Uses of Power Line Communication
- Radio programs transmission.
- Control switching mechanisms in utility companies.
- Protection of transmission line.
- Automatic meter reading.
Some automotive uses are where the data, voice, and music are sent over direct current (DC) battery power line with some special filters.
PLC Advantages
- Low Implementation Cost: PLC does not require any installation of new wires hence reduces the deployment costs.
- Large Reach: PLC enables communication between hard-to-reach nodes where the RF wireless signal suffers from high levels of attenuation like in the underground structures or the buildings with obstructions and metal walls, or the EMI issues in hospitals.
- Lower Running Cost: PLC provides a low-cost solution compared to RF wireless or visible light communication (VLC) systems.
- Indoor High Speed:: Integration between PLC & VLC technology enables high-speed indoor communications.
PLC Disadvantages
- Low transmission speed.
- Sensitivity to disturbance.
- Cross-modulation and nonlinear distortion between channels.
- Large size.
- High price capacitors and inductors used in the PLC system.
Applications for Power Line Communications
- Industrial applications (for irrigation control etc.).
- Lighting applications (for traffic light control, LED dimming etc.).
- Smart Grid and micro-inverters.
- Machine-to-machine applications (vending machines or a hotel's reception-to-room communication).
- Telemetry applications (e.g. offshore oil rigs).
- Transport applications (like for electronics in cars, trains, and airplanes).
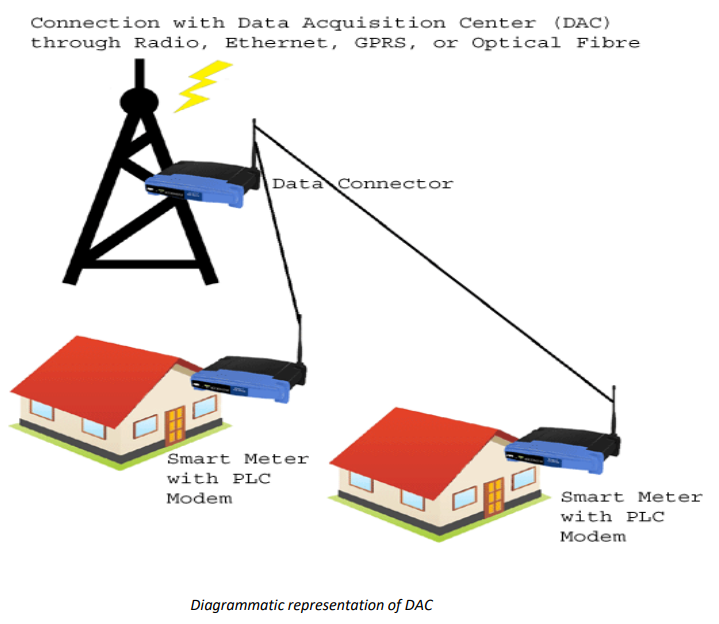
Problems Faced by Power Line Communications
Power wiring in the PLC technology is unshielded and untwisted thus the wiring will emit large amounts of radio energy, causing interference to the existing users of the same frequency band [The BPL (Broadband over Power Line)].
Also, power lines do not necessarily provide a secured media. And, due to the fact that there are numerous elements in each power line network, data attenutation is likely to be a problem. Let's not forget about the fact that a large of amount of electrical noise on the line limits transmission speeds.
References
- Majumder, A. & Caffery, James. (2004). Power line communication: An overview. Potentials, IEEE. 23. 4 - 8. 10.1109/MP.2004.1343222.
- International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 7, July 2014, A Study On Power line communication.
- https://circuitdigest.com - All images
- http://www.ijsrp.org/research-paper-0714/ijsrp-p3152.pdf


