Which type of battery is Suitable for your application? A Comparison Chart
|
|
Lead Acid |
Li-ion Cobalt |
Li-ion Manganese |
Li-ion phosphate |
Li-ion titanate |
Li-Polymer |
NiCad |
NiMh |
Alkaline |
|
Energy Density (Wh/Kg) |
30-50 |
150-250 |
100-150 |
90-120 |
30-110 |
100-130 |
45-80 |
60-120 |
70-80 |
|
Cell Voltage (V) |
2 |
3.6 |
3.7 |
3.2-3.3 |
2.4 |
3.6 |
1.2 |
1.2 |
1.5 |
|
Cycle Life (up to 80% of initial capacity) |
200-300 |
500-1000 |
500-1000 |
1000-2000 |
1000-5000 |
300-500 |
1500 |
300-500 |
~50 |
|
Self- Discharge/ month |
5% |
(3% -protection circuit) |
(3% -protection circuit) |
(3% -protection circuit) |
(3% -protection circuit) |
(3% -protection circuit) |
20% |
30% |
|
|
Charge Time (hrs.) |
8-16 |
2-4 |
1-2 |
1-2 |
2-4 |
1-2 |
2-4 |
2-3 |
|
|
Operating Tempera -ture (C) |
-20 to 60 |
-20 to 60 |
-20 to 60 |
-20 to 60 |
-40 to 55 |
0 to 60 |
-40 to 60 |
-20 to 60 |
0 to 65 |
|
Peak load current |
5C |
2C |
>30C |
>30C |
10C |
>40C |
20C |
5C |
~2C |
|
Safety & Maintenance |
Stable- (3-6) Months (topping charge) |
Protection Circuit mandatory |
Protection Circuit mandatory |
Protection Circuit mandatory |
Protection Circuit mandatory |
Protection Circuit mandatory |
Stable- Fuse protection |
Stable- Fuse protection |
Stable- Fuse Protection |
|
Toxicity |
Very High |
Low |
Low |
Low |
Low |
Very High |
Low |
Low |
Low |
|
Cost |
Low |
High |
High |
High |
High |
High |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Low |
Secondary batteries:
Rechargeable batteries serves a lifesaving option for many devices and systems, but when it comes choosing the right one leads to a confusion which one to be deployed? A comparison chart below gives feature list comparison of different battery chemistries that are widely used, let's get tabular!
Fact: About 70 percent of the world's lithium comes from brine (salt lakes); the remainder is derived from hard rock. Research institutions are developing technology to draw lithium from seawater. Most Li-ion batteries do not contain lithium in metallic form but only in metal oxide. The lithium raw material in a Li-ion battery is only a fraction of one cent per watt, or less than 1 percent of the battery cost. 0.05-1 mg of lithium requires 1 liter of brine/mineral water.
Primary batteries:

Primary (non-rechargeable) batteries plays an important role where charging is impractical and size concerns!
-
Alkaline
Zinc-Carbon
Li-FeS2
Capacity (AA)
1800-2600
400-1700
2500-3500
Discharge rate
low
Very low
Moderate
Shelf life
7 years
1-2 years
10-15 years
Cell Voltage
1.5
1.5
1.5
Cost
Low
Low
Moderate
Fig:
Chart above gives brief comparison on different widely used primary
batteries in different size variations.
Tip: Most of the lithium ion battery fires are caused by separator failure that leads to an electrical short- reasons are high discharge rates, ultra-fast charging – Some suppliers recommend to decrease the charge voltage by:- 100–70% capacity apply the full 4.20V/cell (4.35V/cell or higher for some cells)
- 70–50% capacity reduce the voltage limit to 4.15V/cell (4.35V/cell to 4.25V/cell)
- 50% and lower capacity, decrease the voltage to 3.8V/cell.
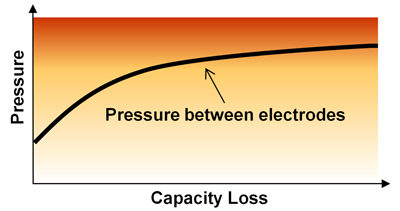
Fig: Pressure increase between electrodes as a function of cycling and state-of-health (SoH)


