- Home heating systems
- Steam turbines
- Oil refining
- Paper drying etc.
"In the boiler furnace, the chemical energy in the fuel is converted into
heat, and it is the function of the boiler to transfer this heat to the
contained water in the most efficient manner."
The flow of a typical boiler plant arrangement is shown in the figure below.
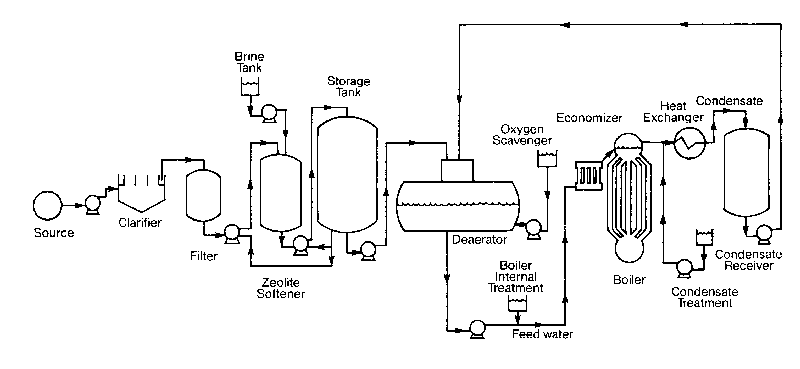
A good boiler system design should be such that:
- It produces superior class steam for use in plants and industrial applications.
- It results in maximum absorption of heat energy produced by the combustion reaction.
There are three means by which heat can be transferred to the water
inside the boiler, i.e. via radiation process, conduction process and
convection process. "The relative percentage of each is dependent upon the
type of boiler, the designed heat transfer surface and the fuels."
The heating surface of a boiler can be defined as the section of boiler which tends to contain hot combustion or flue gases at its one end and liquid on the other. In other words, any metallic component of the boiler which helps in steam generation would be regarded as its heating surface.
Major Parts
A boiler normally consists of following four major sections:
- Burner: This part of the boiler is responsible for commencing the combustion process inside the boiler. It receives electronic signals from the temperature sensing devices like thermostats, as and when the heat needs to be generated out of the system. In most cases, a fuel tank is positioned just next to the boiler for providing fuel source. A filter system is employed to pump the fuel to the boiler. This fuel is then sprayed as fine particles via a nozzle mounted on the burner which tends to produce ignition and combustion reaction inside the chamber.
- Combustion Chamber: The burning of the fuel takes place inside a combustion chamber which is generally constructed of cast iron material. This combustion chamber is designed to experience intense heat energy since the temperature inside the chamber tends to reach very higher limits in a very short period of time. Heat produced inside this chamber is then finally transmitted to the heat exchanger unit.
-
Heat Exchanger:
A sequence of flue passages is used to filter the liquid inside
the combustion chamber in a boiler arrangement. "The pressurized,
boiling water is then pumped through pipes to baseboard heaters or
radiators, which give off the heat energy produced in the boiler."
- Fuel Sources: For its functioning, a boiler consumes variety of fuels such as heating oil, kerosene oil, liquid propane etc.
Main Features
Key features of boilers include:
-
The efficiency offered by a typical boiler system falls between 75%
and 85%. However, advanced boiler systems made up of copper heat
exchangers have now been designed which are capable of providing as
high as 90% efficiency.
- Besides heating applications, a usual boiler system can be employed in many other areas like steam-operated locomotives, external combustion engines and power generation plants.
- In order to get high efficiency out of boiler systems, they must be periodically cleaned and maintained. The maintenance process generally includes activities like making combustion chamber free from useless remains and debris, changing of components such as gaskets and checking of temperature.
- The installation and maintenance of boiler systems must be carried out by professionally skilled and certified personnel. Inappropriate installation and operation of boilers can result in very hazardous effects owing to the severe heat energy involved with them.
- The efficiency of a boiler system also depends upon the total heating surface encompassed by the boiler. More the heating surface more is the efficiency. The heating surface of a boiler is generally represented in square feet.
- As a general rule, horse power rating is used for small boilers and thousands of pounds of steam rating is used for large boilers in industrial applications.
Types of Boilers
In general, there are two major types of boilers available for industrial use:
- Fire Tube Boilers: In this design, the boiler tubes are surrounded by the liquid which needs to be heated whereas the hot gases produced out of combustion reaction are passed via these boiler tubes.
- Water Tube Boilers: Their design is just opposite to fire tube boilers design. Here, the hot combustion gases are circulated around the boiler tubes whereas the tubes enclose the water to be heated.
References
1. Boiler Furnace
2. Boiler Plant_Flow diagram
3.
Heat transfer
4. Heat Exchanger
Sources
Energy Solutioncenter
ehow
CIP