Light overview on the Profibus Protocols
Integration Solutions
Chipkin supports protocol integration across industrial and building automation networks. If you are working on a project that involves multiple protocols (for example, BACnet, Modbus, or industrial Ethernet), the links below provide starting points for tools and integration hardware.

Light Overview of PROFIBUS Protocols
PROFIBUS is a family of industrial communication technologies widely used in automation and process industries. In practical terms, the PROFIBUS ecosystem includes (1) fieldbus variants designed for device-level networks and (2) a related industrial Ethernet technology for higher bandwidth and more modern network infrastructure.
This page provides a concise technical overview of PROFIBUS DP, PROFIBUS PA, and PROFINET. The intent is to help engineers quickly understand where each technology is typically used, what physical media it commonly relies on, and what performance or design considerations are most relevant during selection or integration.
Note on terminology: PROFINET is not a “version of PROFIBUS on Ethernet” in a strict protocol sense; rather, it is a related industrial Ethernet standard from the same ecosystem and is often deployed alongside PROFIBUS networks during modernization and integration projects.
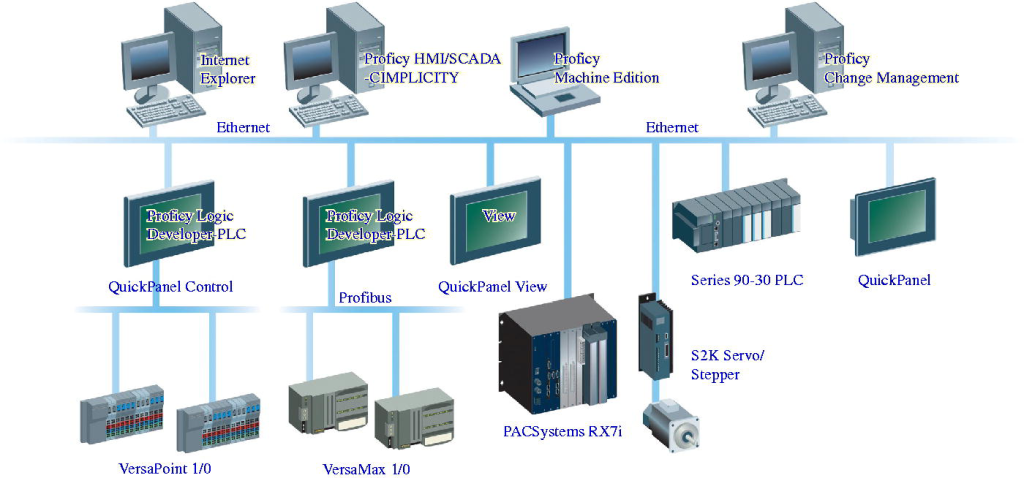
PROFIBUS DP (Decentralized Peripherals)
PROFIBUS DP is commonly used for factory automation, where distributed I/O, drives, and field devices need to be connected to PLCs or controllers with deterministic performance. DP systems are often selected for environments where robust device-level communication is required and where the installation is primarily within non-hazardous areas.
From an implementation perspective, DP networks are typically built on RS-485 physical layers with a bus topology. Devices share the medium, so network design includes considerations such as device count per segment, cable quality, termination, and segmentation using repeaters when required.
Key characteristics commonly associated with PROFIBUS DP include:
- Designed for decentralized I/O and device-level automation networks
- Commonly implemented over RS-485 with a bus topology
- Used broadly in factory automation (typically non-hazardous environments)
- Data rates commonly configured from 9.6 kbit/s up to 12 Mbit/s (implementation dependent)
- Segment device-count and distance constraints may require repeaters/hubs depending on the installation design
- Purple two-core screened cable is commonly associated with PROFIBUS DP installations
- Correct termination and segmentation practices are critical for reliability
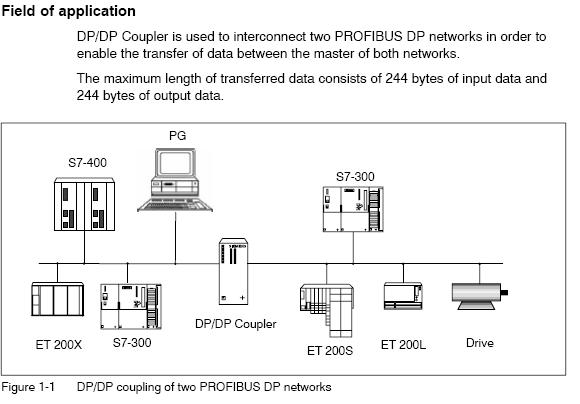
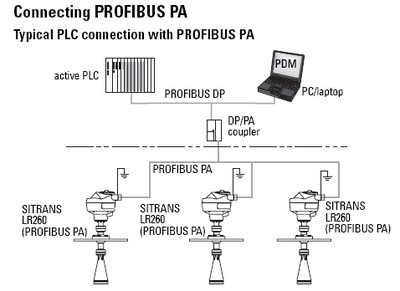
PROFIBUS PA (Process Automation)
PROFIBUS PA targets process automation use cases, such as instrumentation and devices in process industries. PA is often selected where devices are deployed in environments that may require hazardous-area considerations, and where long cable runs and power distribution to field instruments are practical requirements.
A distinguishing feature of PROFIBUS PA is its use of a bus-powered approach that allows both power and communication over the same two-wire cabling. PA systems are designed with reliability and installation constraints in mind, and typically operate at a fixed, lower data rate suitable for process instrumentation.
Key characteristics commonly associated with PROFIBUS PA include:
- Designed for process automation field instrumentation
- Commonly used in environments that may include hazardous/explosive area requirements
- Two-core screened cable is commonly associated with PA installations (often referenced as blue)
- Bus-powered communication approach intended to reduce ignition risk when properly engineered
- Fixed data rate commonly referenced as 31.25 kbit/s for increased robustness (implementation dependent)
- Often integrated with higher-level networks through couplers/links
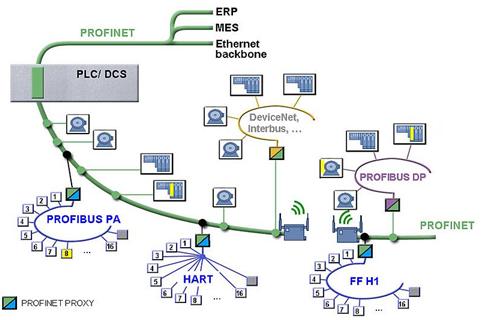
PROFINET (Industrial Ethernet)
PROFINET is an industrial Ethernet technology commonly used for real-time communication between controllers, distributed I/O, drives, and higher-level systems. It is frequently used as a modernization path where Ethernet infrastructure is preferred for bandwidth, plant-wide connectivity, and integration with IT/OT network practices.
In typical deployments, PROFINET devices are identified and managed using network identifiers such as MAC addresses and device names, and they operate over Ethernet infrastructure using standard switching hardware designed for industrial environments. Configuration practices vary by vendor ecosystem, but network engineering commonly includes segmentation, VLANs, and deterministic design practices when real-time behavior is required.
Key characteristics commonly associated with PROFINET include:
- Industrial Ethernet technology used for controller-to-device and system-level communication
- Devices are typically identified using a combination of MAC address and assigned device name
- IP addressing may be used depending on device role and network design
- Supports real-time communication profiles used for automation applications
- Network diagnostics can often be performed using standard Ethernet analysis tools (e.g., packet captures)
- Designed for scalability using Ethernet switching infrastructure
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between PROFIBUS DP and PROFIBUS PA?
PROFIBUS DP is commonly used for factory automation and distributed I/O, typically implemented over RS-485.
PROFIBUS PA is used for process automation and instrumentation, often using bus-powered two-wire installations
and a lower fixed data rate suited to process devices.
Is PROFINET the same as PROFIBUS?
No. PROFINET is an industrial Ethernet technology from the same ecosystem and is often used alongside or as a
modernization path from PROFIBUS networks, but it is not simply “PROFIBUS over Ethernet.”
Why does cable type matter for PROFIBUS?
Fieldbus reliability depends heavily on physical layer design. Cable type, shielding, termination, segment length,
and device count all influence signal integrity and network stability.
When would I choose PROFIBUS versus PROFINET?
Selection typically depends on existing infrastructure, required performance, plant standards, and integration
needs. PROFIBUS is common in legacy or established fieldbus systems, while PROFINET is often chosen where Ethernet
infrastructure and scalable integration are priorities.
Can PROFIBUS and PROFINET be integrated?
Yes. Many automation architectures include both. Integration is commonly performed using couplers, gateways, or
controller modules that bridge data between networks.