RS485 - What Are The Resistor Color Codes
In RS-485 networks, resistors are commonly used for line termination and biasing. Correct resistor values are important for signal integrity, especially on long cable runs or multi-drop networks. These resistor values are identified using standard resistor color codes.
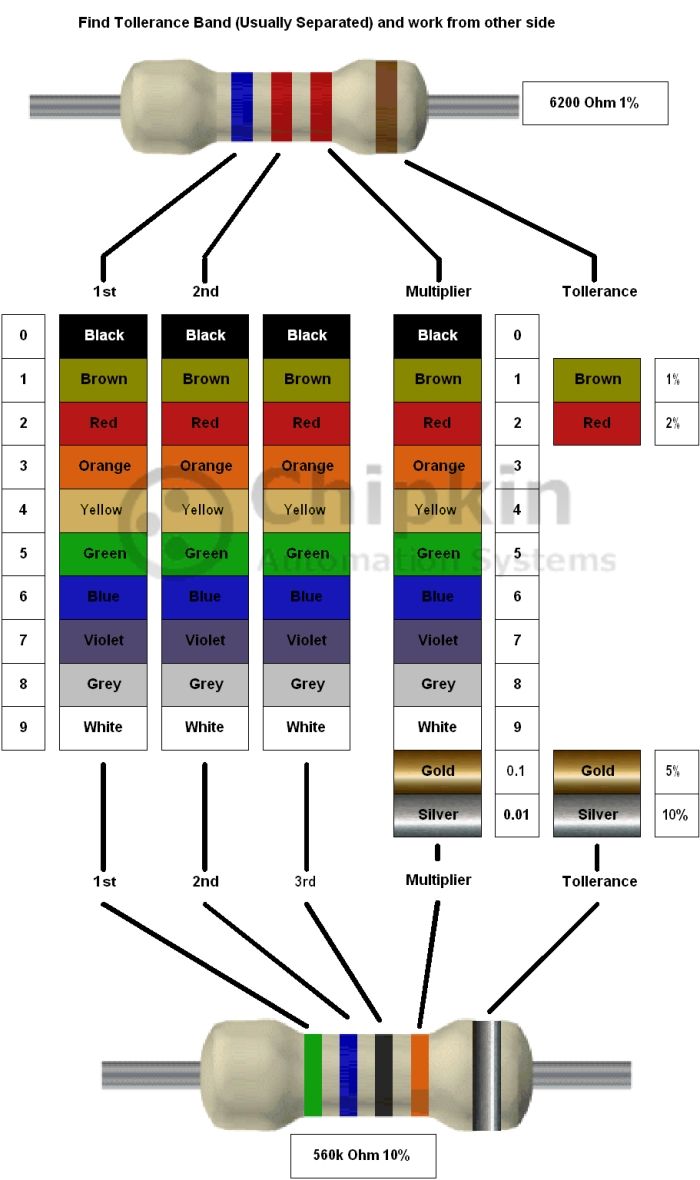
This article provides a quick reference to resistor color codes typically found on 4-band and 5-band resistors, which are the most common types used in RS-485 termination and biasing circuits.
Understanding Resistor Color Codes
Resistor color codes indicate a resistor’s nominal value and tolerance using colored bands printed on the component body. The reading direction starts from the end closest to the first band.
For typical RS-485 applications:
- 4-band resistors encode two significant digits, a multiplier, and a tolerance.
- 5-band resistors encode three significant digits, a multiplier, and a tolerance, allowing for more precise values.
Common RS-485 termination resistors (for example, 120 Ω) and bias resistors can be identified directly from these color codes without needing a meter.
Resistor Color Code Reference Chart
The chart below shows standard color codes for both 4-band and 5-band resistors. This reference applies broadly to resistors used in RS-485 termination, biasing, and general electronics applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Why are resistors important in RS-485 networks?
Resistors are used to terminate the communication line and to provide biasing,
helping prevent signal reflections and undefined logic levels on the bus.
What resistor value is commonly used for RS-485 termination?
A termination resistor of approximately 120 Ω is commonly used, matching
the characteristic impedance of typical RS-485 cabling.
How do I know if a resistor is 4-band or 5-band?
Count the number of color bands on the resistor body. Five-band resistors
generally indicate tighter tolerance or more precise values.