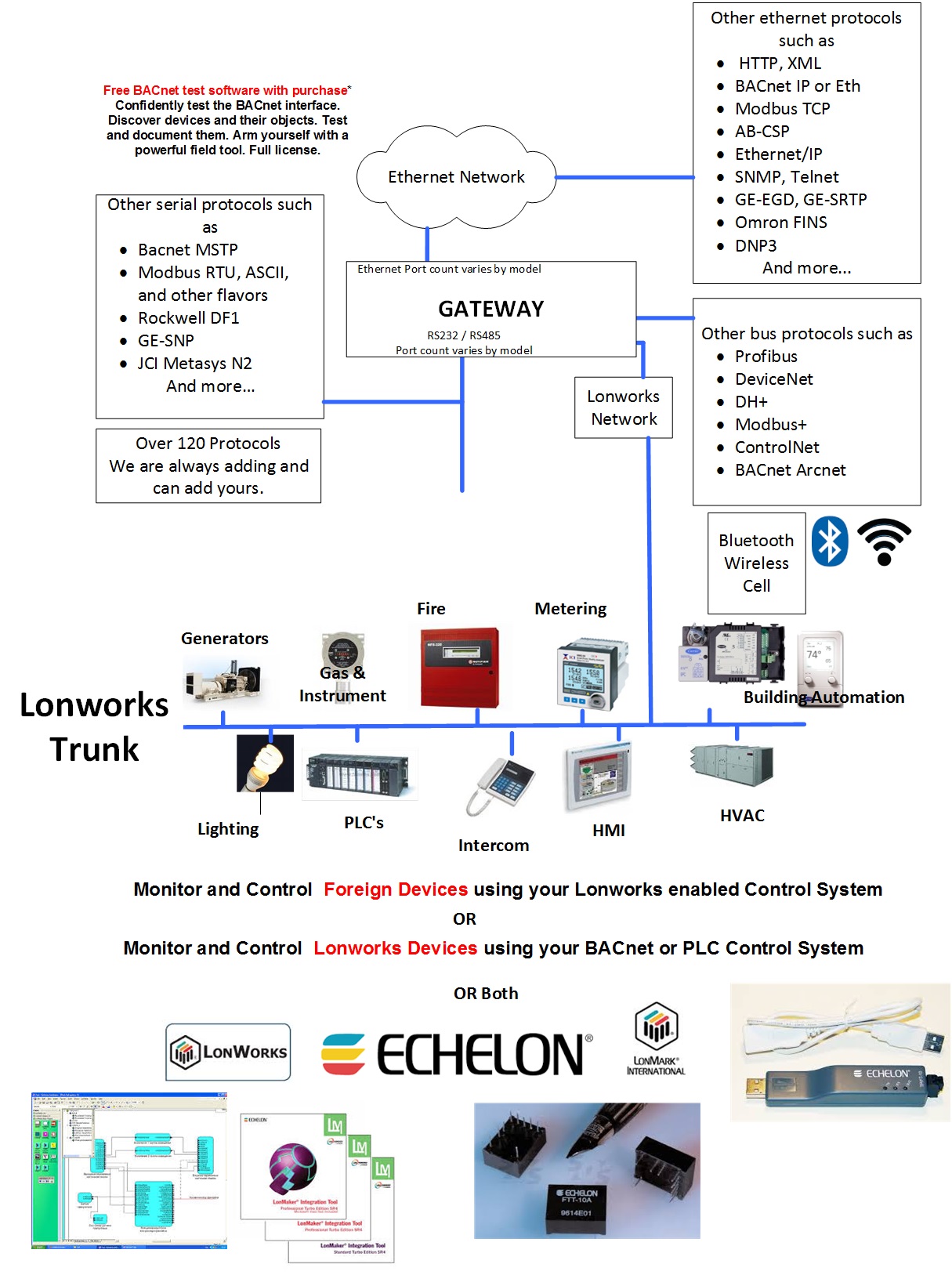
QuickServer Gateway (LonWorks)
QuickServer is a high performance, fully configurable, cost-effective Building and Industrial Automation gateway for integrators to easily interface devices to networks in commercial buildings and industrial plants.
System integrators worldwide have benefitted from the value of the powerful line of interoperability gateways offered by FieldServer. Now, QuickServer adds to that value by running the same robust FieldServer protocol conversion software on a highly cost-effective platform backed by the experience, engineering expertise and proven technical support that integrators have come to expect from FieldServer.
QuickServer is available in two series:
The FS-QS-1X11 Series is preloaded with two BAS drivers (one RS485 serial port, one LonWorks Port, and one Ethernet port) drivers from a choice of at least 150 Protocols. There is a basic QuickServer that can handle up to 250 points and an enhanced QuickServer that can handle 500 points.
The FS-QS-1X21 Series is preloaded with two BAS drivers (one RS232 serial port, one LonWorks Port, and one Ethernet port) drivers from a choice of at least 150 Protocols. There is a basic QuickServer that can handle up to 250 points and an enhanced QuickServer that can handle 500 points.
Each QuickServer includes browser-based tools to make it easy to set-up QuickServer and perform diagnostics including determination of status, network settings, node information, map descriptors and more. The USB flash drive also includes the Discovery utility to determine what FieldServers are on a network.
LonWorks
The LonWorks driver allows the FieldServer to transfer data to and from devices using LonWorks protocol over the TP-FT/10 channel amongst others. The LonWorks FieldServers can emulate either a Server or Client.
The FS-B30, QuickServer, and SlotServer Series FieldServers have a built-in LonWorks Interface and a Fieldbus connection is available on the FieldServer.
The FS-B30 and the SlotServer can handle up to 4096 Network Variables which can be of the Standard Network Variable Types (SNVT) and/or User-defined Network Variable Types (UNVT), and the QuickServer can handle 250 Network Variables (or a limit of 500 for the enhanced model).
Modbus Tek-Air
The Tek-Air Modbus RTU driver allows the FieldServer to transfer data to and from Tek-Air devices over either RS- 232 or RS-485 using the Enhanced Tek-Air Modbus RTU protocol. The driver was developed for Modbus Application Protocol Specification V1.1a" from Modbus-IDA. Modbus_Tekair is the same as Modbus_RTU, except that it has the ability to concentrate bytes of data in a packet to create floating point values. The order in which the bytes are combined and the address range used was developed specifically for the Tek-Air/Modbus interface. To accommodate this, the driver must be configured to poll using odd numbered addresses as two integer registers are used for every floating point value. If this value is stored in a floating point data array, it will be retrievable in the correct format on the Server side. Note that the Tekair "Double" data type is not supported.
The information that follows describes how to expand upon the factory defaults provided in the configuration files
included with the FieldServer.
Specifications
Environment
- Operating Temperature: -40 to 75°C (-40 to 167°F)
- Relative Humidity: 5-90% RH non-condensing
Power Requirements
9-30V DC or 12-24V AC
(RS-422 = 15-30V DC or 12-24V AC)
(M-Bus = 12-24V DC)
Current draw: @ 12V
- FS-QS-1010, FS-QS-12X0: 240 mA
- FS-QS-1011, FS-QS-12X1: 250 mA
Physical Dimensions
- Dimensions (WxDxH): 4.5x2.9x1.6 in. (11.5x7.4x4.1cm
- Weight: 0.4 lbs (0.2 Kg)
- Input voltage: 24 V DC nominal: 10-30V DC
Other
Configuration/Diagnostic utilities
- Capacity: 250 points FS-QS-10X1. (500 points FS-QS-12X1)
- Table, Wall or DIN rail mount
Communication
- Baud: 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200
- Start Bit: 7, 8
- Stop Bit: 1, 2
- Parity: Even, Odd, None
LonMark Certification on the QuickServer FS-QS-1XX1-XXXX
- SPID: 80:00:95:46:00:84:04:01
- Profiles: 0000 - Node object (1), 0001 - Open Loop Sensor Object (5), 0003 - Open Loop Actuator Object (5)
- Ethernet: 1, 2
- Parity: 10/100 BaseT
Approvals
- TUV Approved: to UL 916, EN 60950-1, EN 50491-3 and CSA C22.2 standards
- BTL Mark:
- LonMark Certified: (FS-QS-1011 and FS-QS-12X1)
- RoHS Compliant
- GOST-R Certified
- CE and FCC

Dimensions
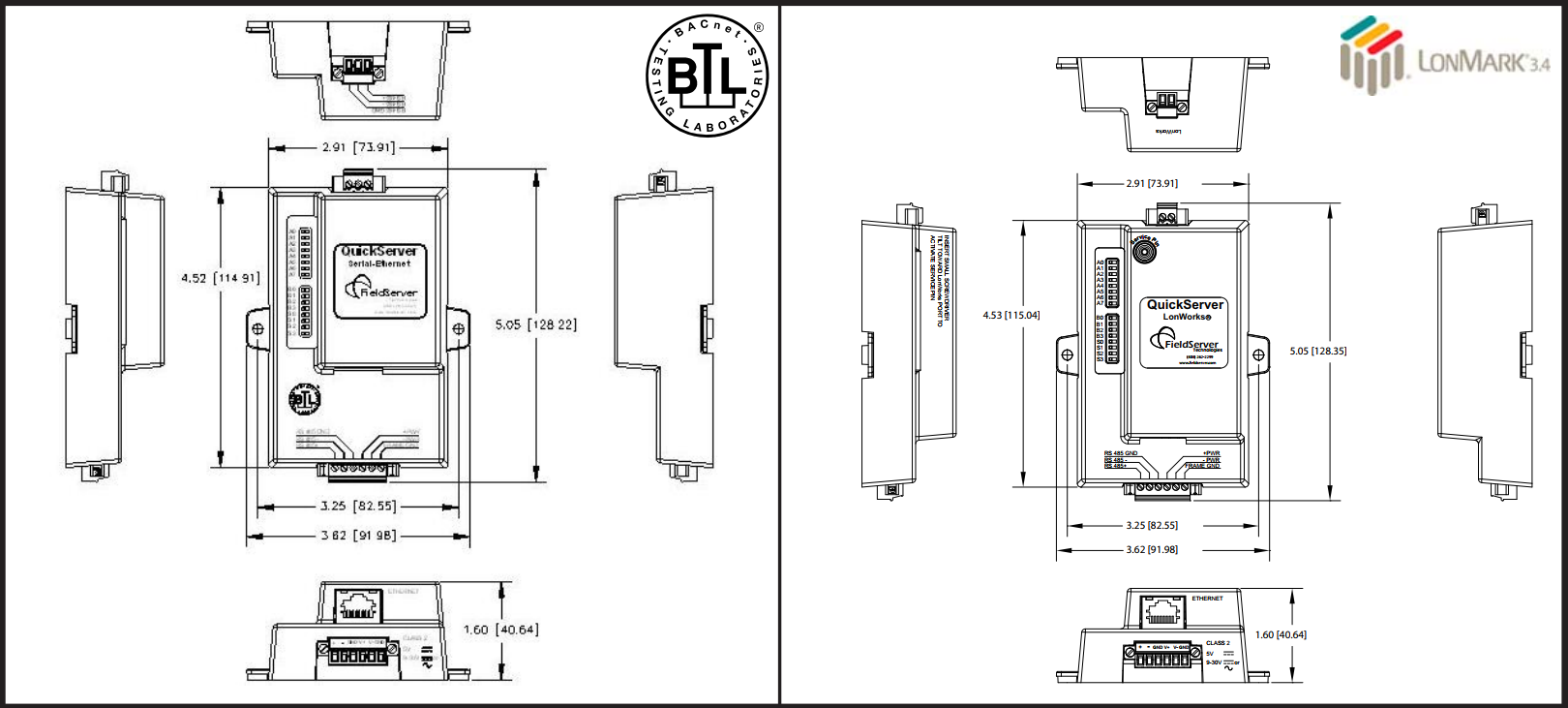
Approvals
FST - Lonworks Approvals
LonMark International
The following FieldServer Platforms are LonMark Certified:
The FieldServer provides the capability of defining multiple functional blocks, but only a single LonMark object. The user can create multiple functional blocks or a LonMark object by filling out the Node SelfDocumentation String and the respective Network Variable Self-documentation String fields in the FieldServer configuration file.
Standards & Certification
LonWorks became and ANSI standard in 1999, and subsequently became a widely adopted global standard. The standard is supported and maintained by LonMark International. Standards include:
ANSI-CEA-709.1-B
ISO-IEC 14908-1
ISO-IEC 14908-2
ISO-IEC 14908-3
ISO-IEC 14908-4
LonMark International is responsible for certification, education, and promotion of interoperability standards for the benefit of manufacturers, integrators, and end users. LonMark International has developed extensive product certification standards and tests to provide the integrator and user with confidence that products from multiple manufacturers can work together.
Sierra Monitors FieldServer has more LonMark Certified gateways for integrators and OEMs that carry the LonMark logo than any other gateway manufacturer. For more information about our LonMark Certified products, visit the LonMark International Product Certification Directory.

https://cdn.chipkin.com/files/web30_prepImages/FST_lonmark_approval_QS.jpg
Tools
Additional Information
Lonworks - LonWorks Protocol
A set of services is offered by the LonWorks Protocol that enables all devices in the network to transmit and receive messages to and from other devices via their application program— requiring no acquaintances with network topology or the other devices’ names, addresses, or functions. Besides, LonWorks Protocol can be made to deliver authentic, high priority messages within delimited transaction times. Moreover Network management services allow remote network management tool’s interaction with devices over the network; making them capable to reconfigure network addresses and parameters, download application programs, report network problems and Start/stop/reset device application programs. Consequently it’s relatively easy to employ LonWorks network over any medium, including power line, twisted pair, radio frequency (RF), infrared (IR), coaxial cable, and fiber optics.
Lonworks is another communications protocol useful in building automation applications. The protocol was developed by the Echelon Corporationin the late 1990s. Lonworks originally transformed from Echelon’s earlier “Lontalk”, and was submitted to the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) for acceptance. Lonworks was designed on a low bandwidth platform for networking devices through powerlines, fiber optics, and other media.
The entire Lonworks package consists of the following components by the Echelon Corporation:
- Lonworks – communications protocol (ANSI/EIA 709.1, and others).
- Echelon’s “Neuron” chip (Three 8-bit inline processor). Two are used by Lonworks, and one as a general application processor.
- Twisted-pair and/or powerline transceivers to transmit Lonworks protocol.
- LNS Network Operating System is the required software.
- Internet connectivity through Standard Network Variable Types (SNVTs) or with LonMark profiles.
- LonMaker allows interoperability among devices.
Lonworks has various advantages and disadvantages. The advantages include:
- Less architecture at the device level.
- Numerous developers of Lonworks products in the market.
- Lonworks devices are close to “plug & play” ability, but still far from achieving interconnectivity in today’s computers using Microsoft Windows.
The disadvantages of Lonworks are presented in the following list:
- Less architecture causes controlled devices and variables to be connected to a separate control device. Most designers do not recommend this type of architecture because network interruptions could eventually produce system failures.
- The protocol is proprietary, and not truly open to the public. Only actual members, mostly manufacturers are included in standard development(s).
- Extensions within Lonworks are allowable only through the LonMark Consortium.
- Hardware specific, and requires the Neuron chip for network movement of the protocol.
Lonworks - LonWorks Applications
Amongst the extensive range of LonWorks technology applications the vital nine are listed below:
- Semiconductor manufacturing
- Lighting control systems
- Energy management systems
- Heating/ventilation/air-conditioning systems
- Security systems
- Home automation
- Consumer appliance controls
- Public street lighting, monitoring, and control
- Gas station control
Lonworks - Building Control Networks
A P2P (peer to peer) architecture is undoubtedly the preeminent way to build control networks. Being exclusive of a single master control, P2P-based control network confers high reliability and high performance to its users. Unlike other control networks, in P2P architectures, there is absolutely free and open communication between network devices which automatically puts a stop to the system collapses that could occur whenever the master stops working.
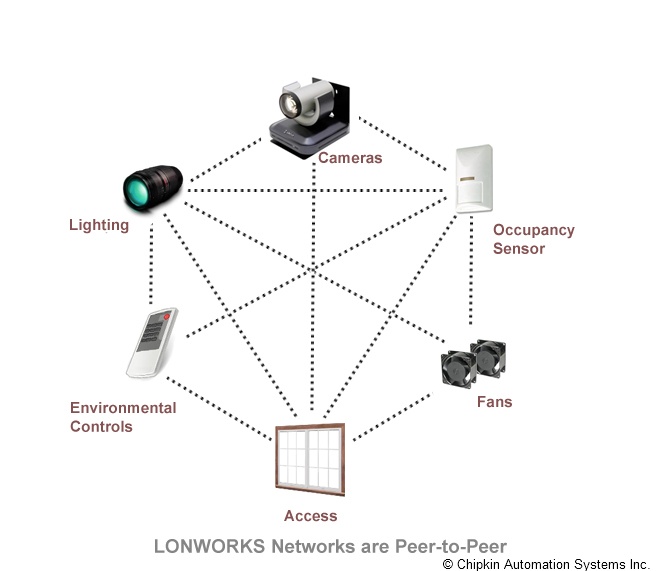
Lonworks - Neuron
A processor identified as Neuron chip embracing three 8- bit inline processors designed by Echelon is well optimized for control network devices. Out of three processors: two are committed for the communications protocol and one is a general-purpose applications processor. Standardization of the variables used to illustrate physical things to LonWorks is maintained by LonMark International and each standard is known as Standard Network Variable Types (SNVTs). LNS Network Operating System is a mandatory software component of open control systems which ensures an open environment for extending, maintaining, and managing LonWorks based system
Lonworks - Introduction
LonWorks is not just a protocol or physical layer for communication but an exclusively designed networking technology platform to install, maintain, monitor and sense various automation and control applications. Essentially LonWorks was established for a range of automation functions within buildings such as lighting and HVAC. Invented by Echelon Corporation, the fundamental communications platform, twisted pair signaling technology, power line signaling technology, and IP tunneling method constitutes a global standard documented ISO/IEC 14908.
Lonworks - Software - NodeUtil
What happens if you need to learn about a Lonworks network and it devices but you haven’t been provided with the database or if you don’t have LonMaker?
NodeUtilis a Lonworks utility that can be used to explore Lonworks networks and devices without having LonMaker. All you need is a device such as an Echelon U10/U20 USB Network Interface.

Using NodeUtil you can discover devices, learn about the Domains, SubNets, NodeID’s. You can also upload the XIF file from specific nodes.
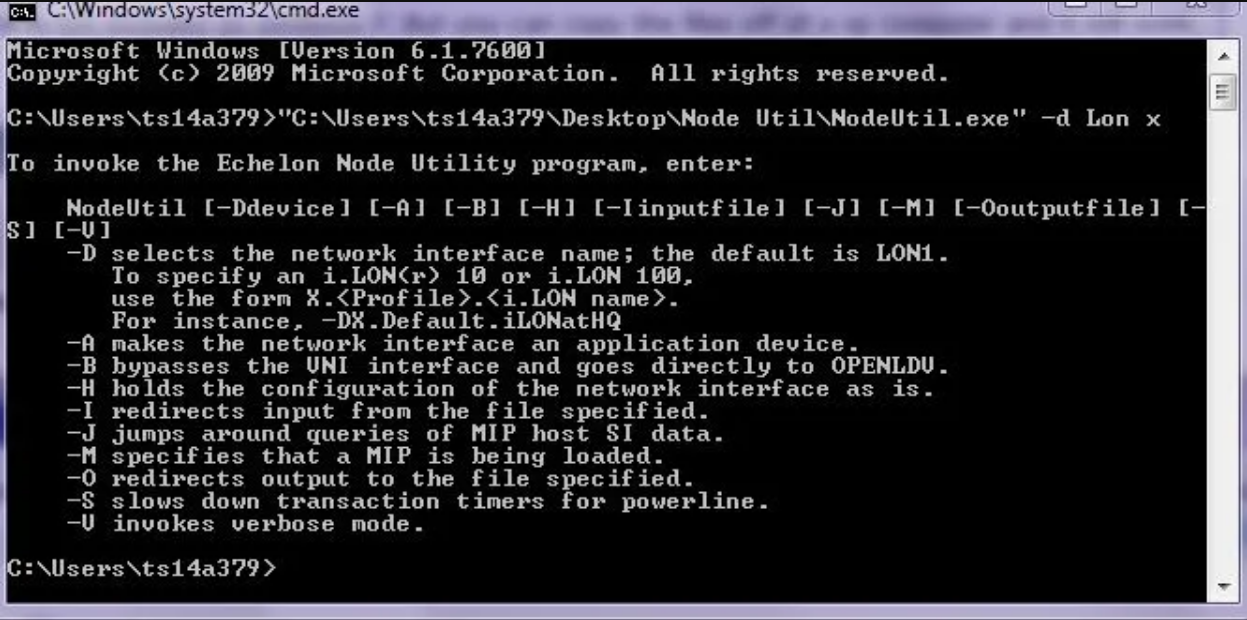
Download NodeUtil:
- Download unavailable: NodeUtil 3.51 and NodeLoad 2.16 Utilities
- NodeUtil Node Utility 3.23
- NodeUtil Node Utility 2.21
- NodeUtil Node Utility 2.04
- NodeUtil Node Utility 1.82
- U10/U20 USB Network
Interface driver for Linux
- Redhat Linux 9 (Fedora Core 3 or Fedora Core 4) network interface driver for the Echelon U10/U20 USB Network Interfaces. This network interface driver depends upon the libftdi, libusb and hotplug libraries which are normally built into the Fedora kernel; the binary driver distribution includes the libftdi and libusb libraries in case they are not loaded into the kernel already. See the Read Me for more information and installation instructions. - U10/U20 USB Network
Interface driver for Mac OS X
- Mac OS X 10.4 (or higher) network interface driver for the Echelon U10/U20 USB Network Interfaces. Includes ready-to-use NodeUtil application and ported headers for developing your own OpenLDV compatible applications. - NodeUtil and NodeLoad User’s Guide
Downloads retrieved from: https://www.echelon.com/resource-library-results?q=NodeUtil
Lonworks - Software - Lonmaker
LonMaker is a Windows GUI based network/device management tool for Echelon LonWorks. It can be used for initial network setup and functioning as a management console on a completed network.
Purchase from Echelon.
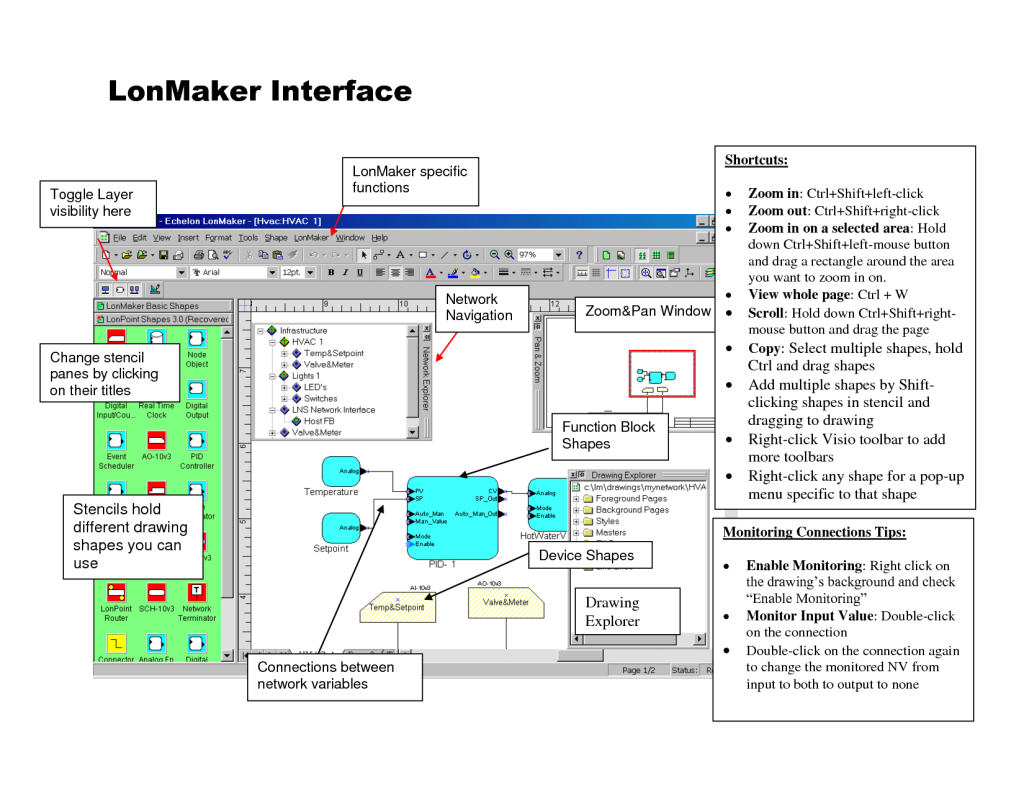
Lonworks - Why are Lonworks communications so good
The communications between all Lonworks devices is done by means of a proprietry chip (The Neuron chip) made according to one design by one company according to one standard which it wrote on its own. It’s obvious that there are so many less aspects of the data communications process that can go wrong when there is a single entity involved. When a device vendor implements a Lonworks System Interface he simply has to implement the application layer of the data communication process. For almost all other protocols the device vendor must implement the physical layer, data link layer, the Network Layer, The transport Layer, The Session Layer, the Presentation Layer and the Application Layer. You can see how many more areas of risk there are.
When Echelon released the standard, their license terms required anyone who implements it to implement the full standard. The fact that other vendors can’t cherry pick features and services means that even when implemented by other vendors you still have the same strong chance of success.
Lonworks - Jargon Watch
Lonworks – a wide ranging term generally applied to describe the whole technology developed by Echelon. It is used frequently and ambiguously.
LonTalk – A registred trademark belonging to Echelon. They use it as the name of the protocol used for data communications in a Lonworks system. Ie. It is the brandname protocol. Echelon released this protocol so it could be adopted as a standard – ANSI-approved standard EIA/CEA-709.1-A-1999 – SO/IEC Standard 14908 or European standard EN14908.
Lonworks - How to - Commissioning and Binding
How to Commission and Bind using Lonmaker. CAS can configure Lonworks gateways so Commissioning and Binding can be avoided. Call our Tech Sipport for more info.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u_mzAdszviI
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w3QeimYx94I
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H76n1-lcrhI
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SEcAx6xy3is
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dFyyKNmGVB4
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B_Cs1clgNzM
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=29cuWwVKNdA
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vm2Ss72C5bg
Lonworks - Software - XIFdump
Another useful utility is XIFDUMP. It is a report generator (DOS), and it allows you to generate reports (text file) from a XIF files.
Download XIFDUMP:
Logos





__77623.1769027873.png?c=2)