KNX Application Examples
KNX Protocol - 10-Minute Course
KNX is a widely adopted open standard for building automation, used across residential, commercial, and industrial environments. Its flexibility allows the same protocol to support small private dwellings as well as large, complex facilities. This page presents practical KNX application examples to illustrate how the protocol is deployed in real-world scenarios.
These examples focus on typical KNX use cases rather than specific vendor implementations. They are intended to help system designers, integrators, and engineers understand how KNX devices are combined into functional systems and how those systems scale across different building types.
KNX is commonly used alongside gateways and integration devices, such as protocol converters, to connect KNX networks with higher-level building management systems (BMS) or supervisory platforms.
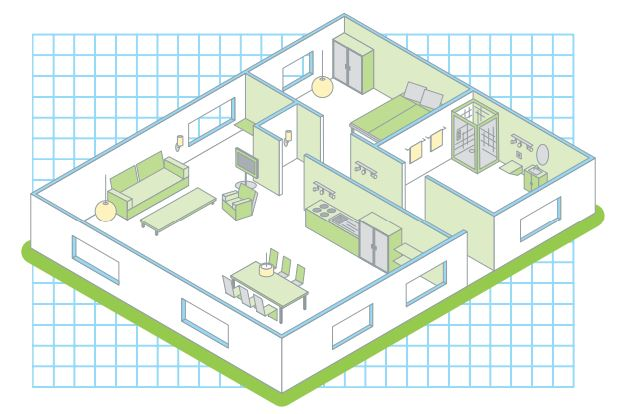
Example 1: KNX Application in a Private Residence
In residential environments, KNX is often used to provide centralized yet flexible control of lighting, heating, shading, and other comfort-related systems. Devices communicate over the KNX bus, allowing wall switches, sensors, and actuators to exchange information without relying on a central controller.
A typical private flat or home installation may include:
- KNX lighting actuators controlling multiple lighting circuits
- Wall-mounted KNX switches or touch panels
- Temperature sensors and thermostatic controllers
- Blind and shutter actuators for daylight control
These components are configured using group addresses, enabling flexible associations between inputs and outputs. Changes to control logic can often be made through configuration rather than rewiring, which is a key advantage of KNX in residential automation.
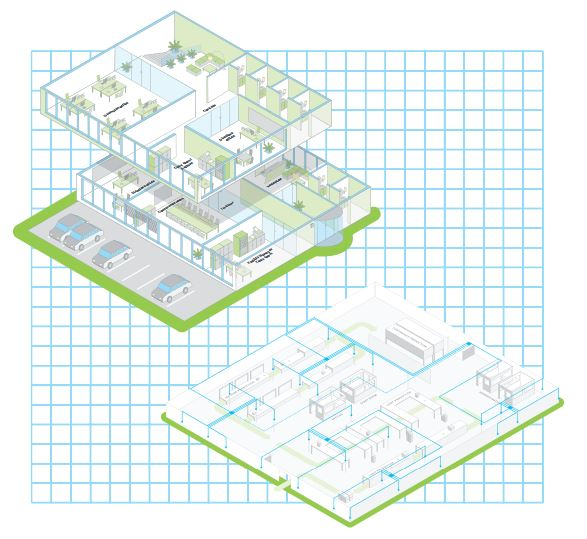
Example 2: KNX Application in an Industrial or Commercial Building
In larger buildings, KNX is frequently used as a field-level automation protocol that integrates with supervisory control systems. Industrial and commercial installations place greater emphasis on scalability, maintainability, and integration with other building services.
Typical KNX use cases in these environments include:
- Lighting control across multiple zones or floors
- Integration with HVAC systems for occupancy-based control
- Energy monitoring and load management
- Interface with centralized BMS platforms
In these scenarios, KNX networks are often connected to other protocols through gateways, allowing KNX data points to be monitored or controlled from higher-level systems. This approach preserves the strengths of KNX at the device level while enabling centralized supervision.
Additional KNX Application References
KNX is supported by a large ecosystem of manufacturers and solution providers. Additional application examples and reference architectures are published by industry vendors and organizations.
One such reference document is available here:
KNX Application Examples (External Reference)
External documents are provided for reference only and may reflect specific vendor implementations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can KNX be used in both homes and industrial buildings?
Yes. KNX is designed to scale from small residential installations to large commercial and industrial
buildings using the same underlying protocol principles.
Does KNX require a central controller?
No. KNX is a distributed system. Devices communicate directly over the KNX bus using group addresses.
How does KNX integrate with other building systems?
KNX networks are commonly integrated using gateways that expose KNX data to other protocols or supervisory
systems.
Is KNX suitable for retrofits?
Yes. Depending on the installation medium (twisted pair, IP, powerline, or RF), KNX can be applied in both
new construction and retrofit projects.


