KNX Overview A 10-Minute Course
KNX Protocol - 10-Minute Course
This article provides an overview of KNX as a building and home automation communications standard. KNX is an OSI-based network communications protocol designed for interoperable control of building systems such as lighting, HVAC, blinds/shutters, security, metering, and supervisory visualization. KNX is used in both residential and commercial automation environments where multi-vendor interoperability is required.
The term KNX is derived from “Konnex.” The KNX standard evolved from earlier European building automation technologies, including EIB (European Installation Bus), EHS (European Home Systems), and BatiBUS. KNX defines common communication mechanisms and data models so that devices from different vendors can exchange control information using standardized addressing and telegram formats.
KNX is not tied to a single hardware platform. KNX devices can be implemented on a wide range of hardware depending on the intended application and required feature set, from low-resource embedded controllers to supervisory software running on a PC.
Supported Communication Media
KNX supports multiple physical and transport media. The choice of medium affects installation practices, bandwidth, commissioning workflow, and the types of devices that can be integrated. Common KNX media include:
- Twisted Pair (TP) – A commonly deployed medium for KNX field devices. It is used for distributed control wiring and supports telegram exchange between devices on the bus.
- Radio Frequency (RF) – Used for wireless KNX deployments where running cable is difficult or undesirable.
- Power Line (PL) – Uses existing mains wiring for communication in some installations.
- IP/Ethernet (KNXnet/IP) – Used for backbone networking, tunneling, and routing between KNX line segments and IP-based systems.
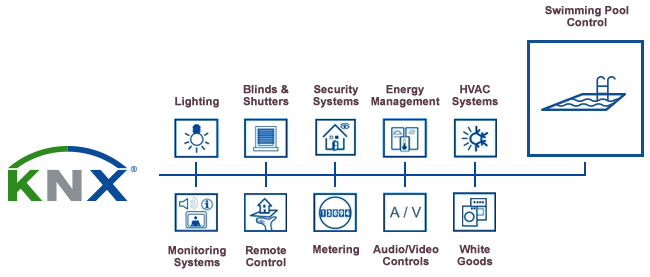
In many practical designs, twisted pair is used at the field level while KNXnet/IP is used for higher-level backbone connectivity, remote access, or integration into IP-based building networks.
Typical KNX Applications
KNX is used to implement distributed automation where sensors, actuators, and supervisory systems exchange control telegrams. Applications span multiple building subsystems and typically include:
- Lighting control (switching, dimming, scene control)
- HVAC control and integration (setpoints, modes, scheduling, status)
- Blind and shutter control
- Security and alarm signaling (where supported by the installation design)
- Energy monitoring and metering integration
- Visualization and supervisory control interfaces
KNX installations often combine local control behavior (implemented in devices on the bus) with higher-level supervisory functions. Because KNX is designed as a standardized multi-vendor system, commissioning and troubleshooting commonly involve understanding addressing, group objects, and the configured behavior of devices in the installation.
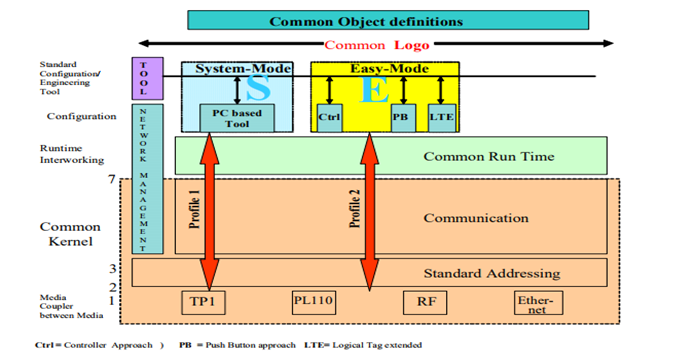
Fig: KNX Model
KNX Overview FAQ
What is KNX?
KNX is a standardized communications protocol used for building and home automation. It defines how devices
exchange control and status information for systems such as lighting, HVAC, and blinds.
What does KNX stand for?
KNX is derived from “Konnex.” It is the name of the standardized protocol and ecosystem rather than an
acronym describing a specific physical layer.
What technologies contributed to KNX?
KNX evolved from earlier systems including EIB (European Installation Bus), EHS (European Home Systems), and
BatiBUS.
What physical media can KNX use?
KNX can operate over twisted pair, radio frequency, power line, and IP/Ethernet (KNXnet/IP). The selected
medium depends on the installation and system architecture.
Where is KNX commonly used?
KNX is used in residential and commercial buildings for control and integration of lighting, HVAC, blinds,
energy monitoring, and supervisory visualization.

